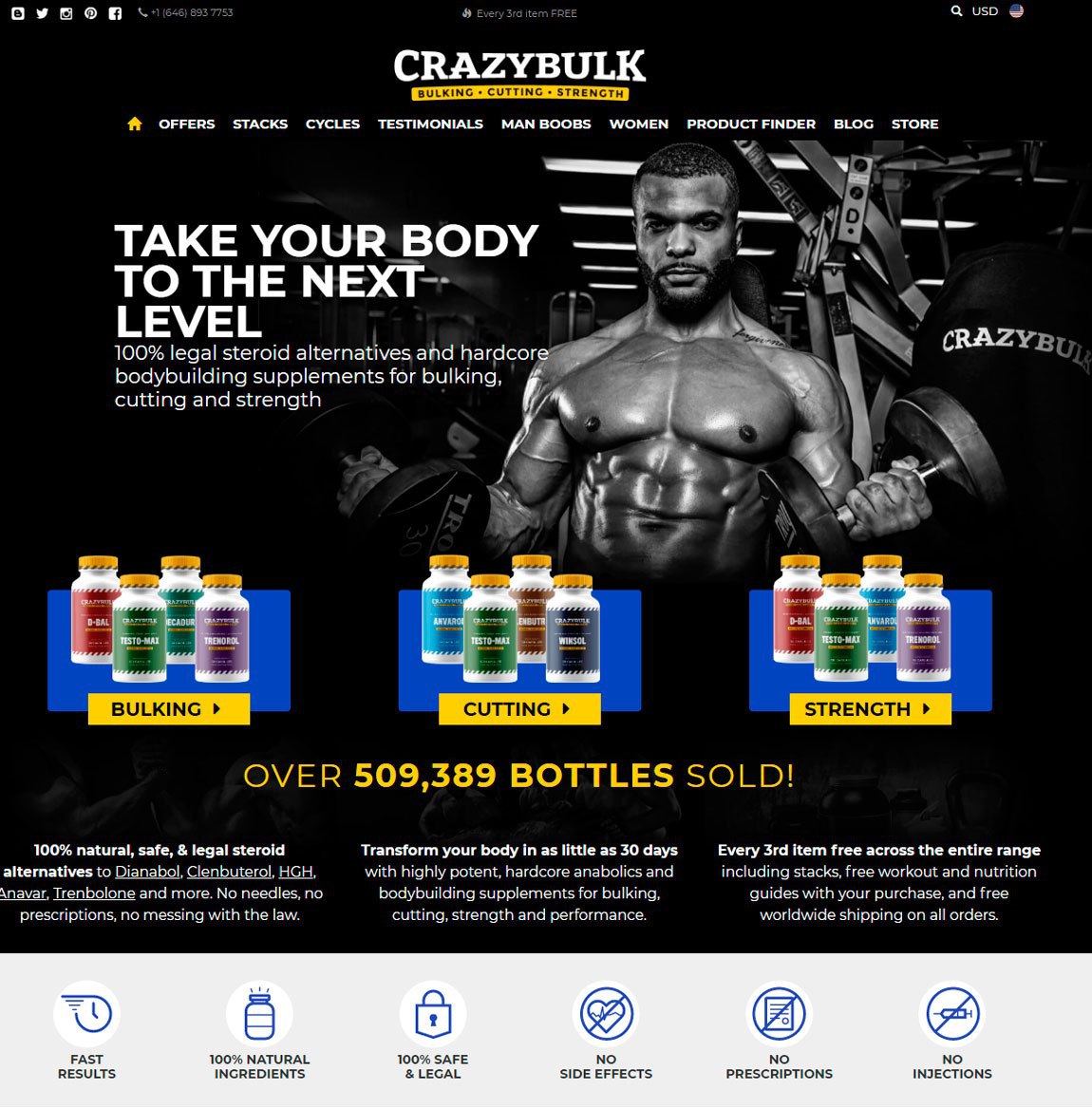
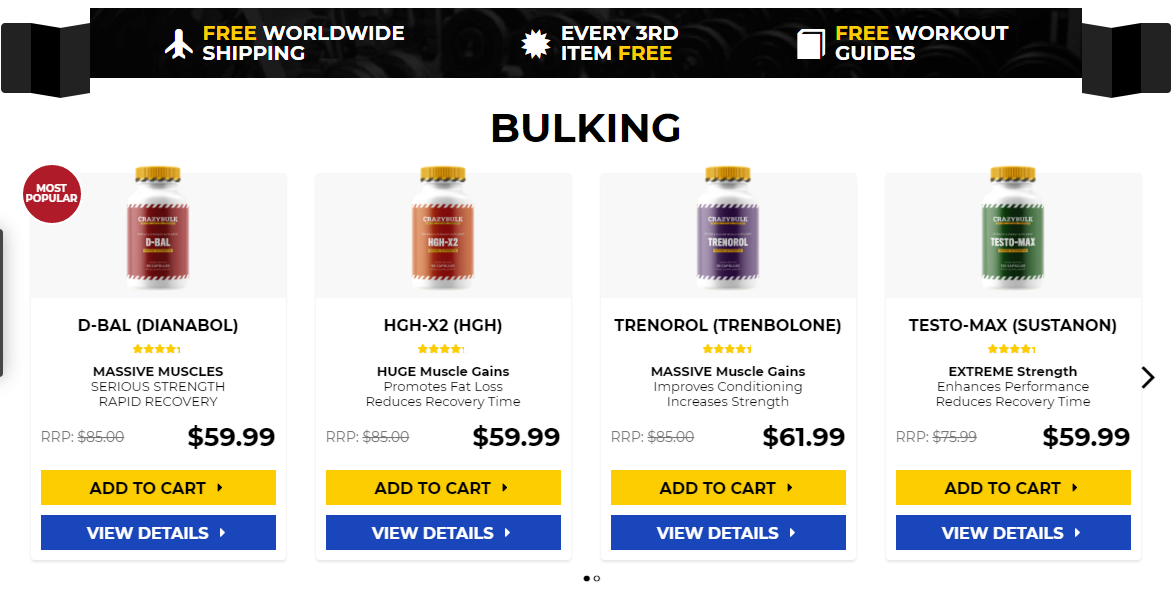
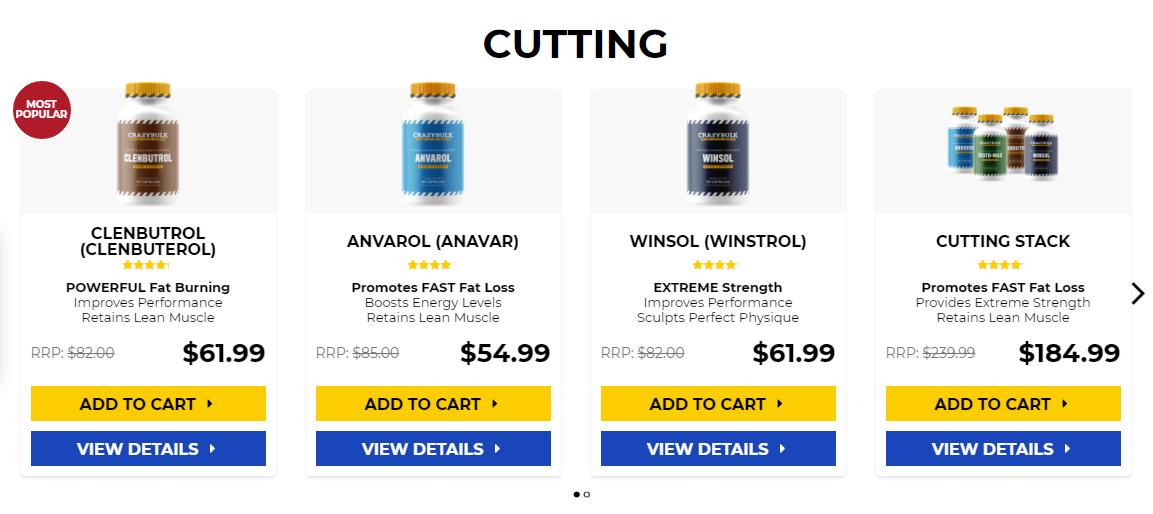
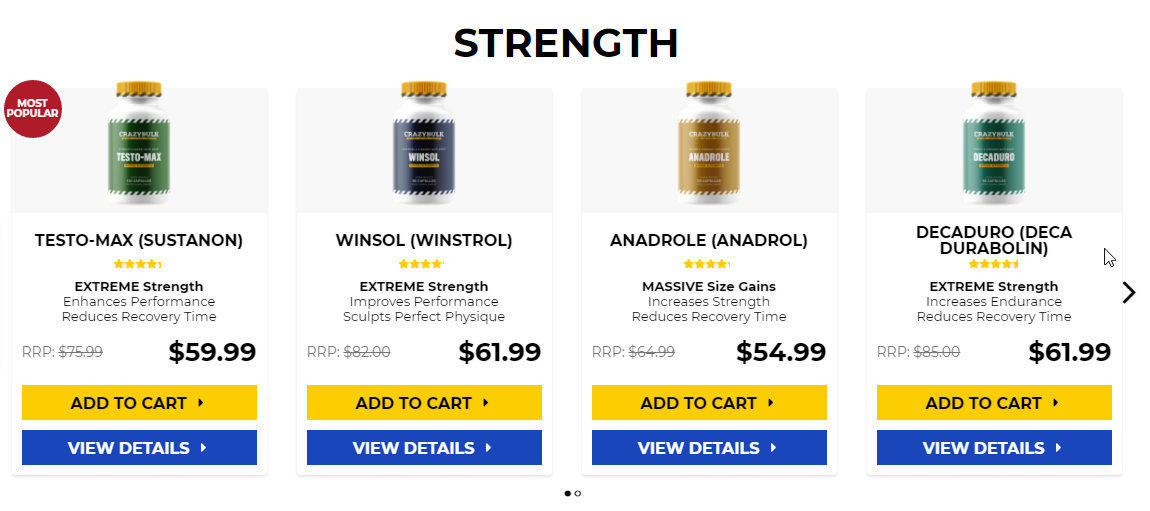
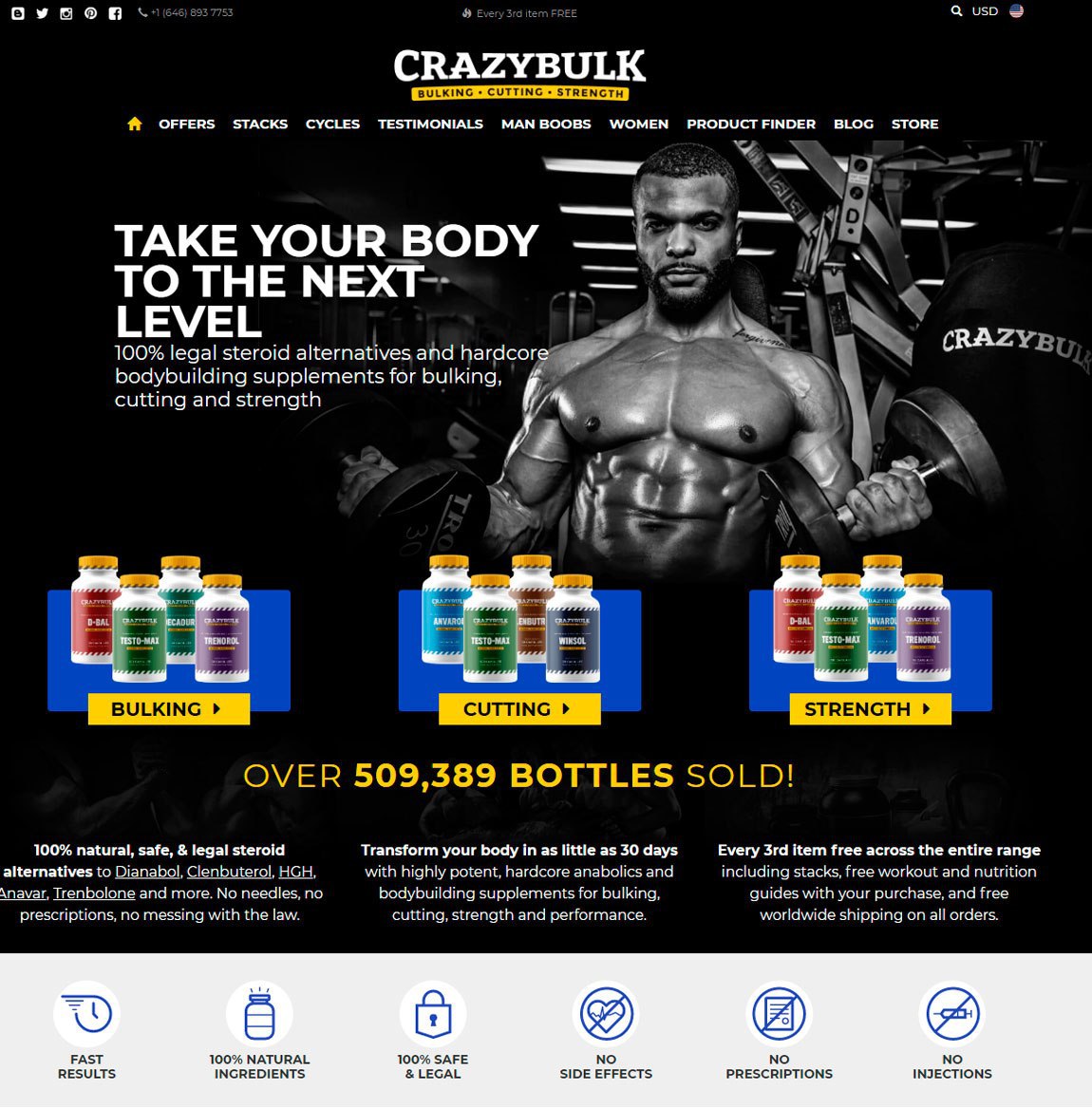
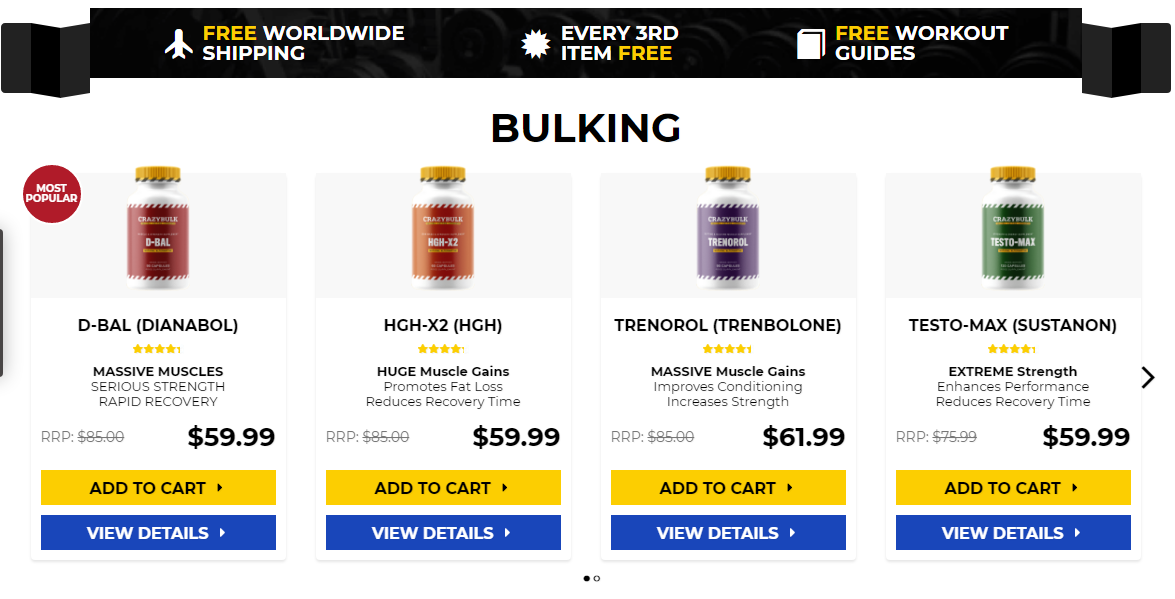
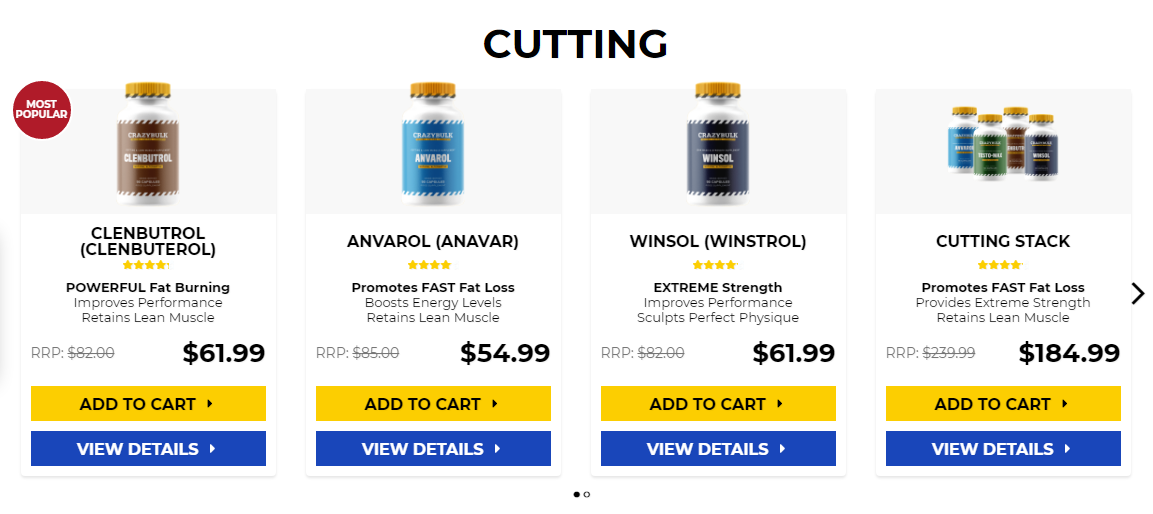
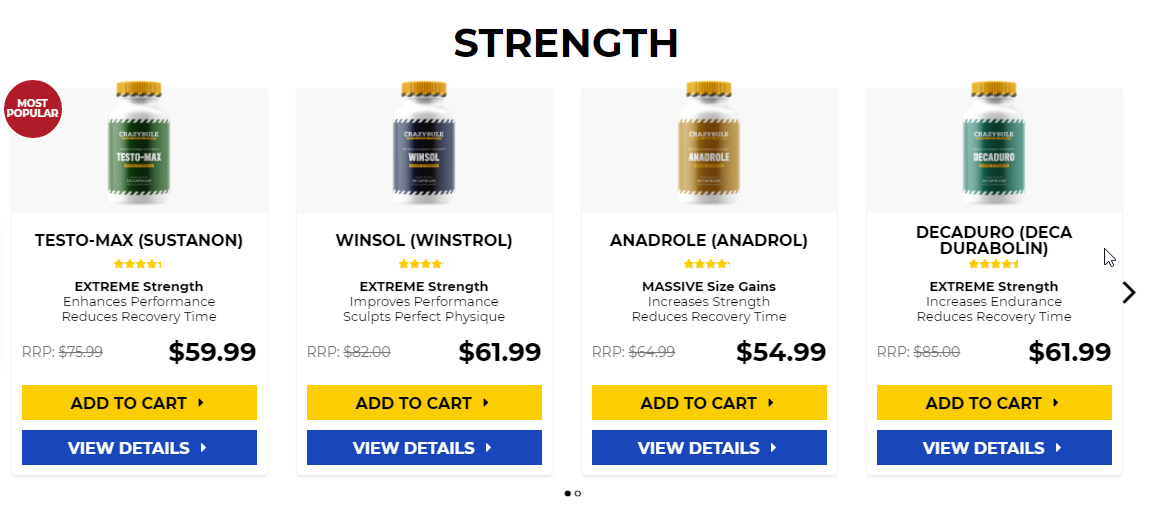
Testosterone level 400 low, testosterone levels by age graph – Legal steroids for sale

Testosterone level 400 low
Equatorial Guinea Supreme Court judges appointed by the president for 5-year terms; Constitutional Court members appointed by the president Eritrea High Court judges appointed by the president Estonia the chief justice is proposed by the president and appointed by the Riigikogu; other justices proposed by the chief justice and appointed by the Riigikogu; justices appointed for life Ethiopia president and vice president of Federal Supreme Court nominated by the prime minister and appointed by the House of People’s Representatives; other Supreme Court judges nominated by the Federal Judicial Administrative Council and appointed by the House of People’s Representatives; judges serve until retirement at age 60 Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) all justices appointed by the governor; tenure specified in each justice’s instrument of appointment Federated States of Micronesia justices appointed by the president of the Federated States of Micronesia with the approval of two-thirds of Congress; justices appointed for life Fiji chief justice appointed by the president of Fiji on the advice of the prime minister following consultation with the parliamentary leader of the opposition; judges of the Supreme Court, the president of the Court of Appeal, the justices of the Court of Appeal, and puisne judges of the High Court are appointed by the president of Fiji, upon the nomination of the Judicial Service Commission, after consulting with the cabinet minister and the committee of the House of Representatives responsible for the administration of justice; the chief justice, Supreme Court judges, and justices of Appeal generally required to retire at age 70, but may be waived for one or more sessions of the court; puisine judges appointed for not less than 4 years nor more than 7 years with mandatory retirement at age 65 Finland Supreme Court and Supreme Administrative Court judges appointed by the president of the republic; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 65 France Court of Cassation judges appointed by the president of the republic from nominations from the High Council of the Judiciary, presided by the Court of Cassation and 15 appointed members; judge term of appointment NA; Constitutional Council members appointed – 3 by the president of the republic and 3 each by the National Assembly and Senate presidents; members serve 9-year, non-renewable terms with one third of the membership renewed every 3 years Gabon Supreme Court judges appointment and tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed – 3 by the national president, 3 by the president of the Senate, and 3 by the president of the National Assembly; judges serve 7-year, single renewable terms Georgia Supreme Court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the Parliament; judges serve not less than 10-year terms; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president following candidate selection by the Justice Council of Georgia, a 12-member consultative body of high-level judges, and presidential and parliamentary appointees; judges appointed for 10-year terms Germany Federal Court of Justice judges selected by the Judges Election Committee, which consists of the Secretaries of Justice from each of the 16 federated States and 16 members appointed by the Federal Parliament; judges appointed by the president of Germany; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 65; Federal Constitutional Court judges – one-half elected by the House of Representatives and one-half by the Senate; judges appointed for 12-year terms with mandatory retirement at age 68 Ghana chief justice appointed by the president in consultation with the Council of State (a small advisory body of prominent citizens) and with the approval of Parliament; other justices appointed by the president upon the advice of the Judicial Council (an 18-member independent body of judicial, military and police officials, and presidential nominees) and on the advice of the Council of State; justices can retire at age 60, with compulsory retirement at age 70 Gibraltar Court of Appeal and Supreme Court judges appointed by the governor upon the advice of the Judicial Service Commission, a 7-member body of judges and appointees of the governor; tenure of the Court of Appeal president based on terms of appointment; Supreme Court chief justice and judge normally appointed until retirement at age 67, but can be extended 3 years Greece judges selected by the Supreme Judicial Council which includes the president of the Supreme Court, other judges, and the prosecutor of the Supreme Court; judges appointed for life following a 2-year probationary period Greenland judges appointed by the monarch upon the recommendation of the Judicial Appointments Council, a 6-member independent body of judges and lawyers; judges appointed for life with retirement at age 70 Grenada justice selection and tenure NA Guam justices appointed by the governor and confirmed by the Guam legislature; justices appointed for life subject to retention election every 10 years Guatemala Supreme Court magistrates elected by the Congress of the Republic from candidates proposed by the Postulation Committee, an independent body of deans of the country’s university law schools, representatives of the country’s law associations, and representatives of the Court of Appeal and other tribunals; magistrates elected for renewable 5-year terms; Constitutional Court judges – 1 elected by the Congress of the Republic, 1 by the Supreme Court president, 1 by the president of the republic, 1 by the University of San Carlos, and one by the BAR association; judges elected for concurrent 5-year terms; the presidency of the court rotates among the magistrates for a single 1-year term Guernsey Royal Court Balliff, Deputy Balliff and Court of Appeal justices appointed by the British Crown and hold office at Her Majesty’s pleasure; jurats elected by the States of Election, a body chaired by the Balliff and a number of jurats Guinea court first president appointed by the national president after consultation with the National Assembly; other members appointed by presidential decree; member tenure NA Guinea-Bissau judges nominated by the Higher Council of the Magistrate, a major government organ responsible for judge appointments, dismissals, and discipline of the judiciary; judges appointed by the president with tenure for life Guyana Court of Appeal and High Court chief justices appointed by the president; other judges of both courts appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a body appointed by the president; judges appointed for life with retirement at age 65 Haiti judges appointed by the president from candidate lists submitted by the Senate of the National Assembly Holy See (Vatican City) cardinal prefect appointed by the Pope; the other 2 cardinals of the court appointed by the cardinal prefect on a yearly basis Honduras court president elected by his peers; judges elected by the National Congress from candidates proposed by the Nominating Board, a diverse 7-member group of judicial officials, other government and non-government officials selected by each of their organizations; judges elected by Congress for renewable, 7-year terms Hong Kong all judges appointed by the Hong Kong Chief Executive upon the recommendation of the Judicial Officers Recommendation Commission, an independent body consisting of the Secretary for Justice and other judges, judicial and legal professionals; permanent judges appointed until normal retirement at age 65, but can be extended; non-permanent judges appointed for renewable 3-year terms without age limit Hungary Curia president elected from among its members for 9 years by the National Assembly on the recommendation of the president of the republic; other Curia judges appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the National Council of Justice, a separate 15-member administrative body; all judges serve until the normal retirement age; Constitutional Court members elected by two-thirds vote of the National Assembly; members serve 12-year terms Iceland judges proposed by Ministry of Interior selection committee and appointed by the president; judges appointed for an indefinite period India justices appointed by the president to serve until age 65 Indonesia Supreme Court judges nominated by Judicial Commission, appointed by president with concurrence of parliament; judges serve until retirement age; Constitutional Court judges – 3 nominated by president, 3 by Supreme Court, and 3 by parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70 Iran Supreme Court president appointed by the head of the Supreme Judicial Council in consultation with judges of the Supreme Court; president appointed for a 5-year term; other judge appointments and tenure NA Iraq Federal Supreme Court and Court of Cassation judges appointed by the Higher Juridical Council, a 26-member independent committee of judicial officials; FSC members appointed for life ; Court of Cassation judges appointed for 1-year probationary period and upon satisfactory performance may be confirmed for permanent tenure until retirement at age 63 Ireland judges nominated by the prime minister and Cabinet and appointed by the president; judges serve till age 70 Isle of Man judges appointed by the Lord Chancellor of England on the nomination of the lieutenant governor; judge tenure NA Israel judges selected by the Judicial Selection Committee, made up of all three branches of the government and chaired by the Minister of Justice; judges can serve up to mandatory retirement age of 70 Italy Supreme Court judges appointed by the Superior Council of the Judiciary, headed by the president, to serve NA terms; Constitutional Court judges – 5 appointed by the president, 5 elected by parliament, 5 elected by select higher courts; judges serve up to 9 years) Jamaica chief justice of the Supreme Court and president of the Court of Appeal appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the prime minister; other judges of both courts appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the Judicial Service Commission; judges of both courts serve till age 70 Japan Supreme Court chief justice designated by the Cabinet and appointed by the monarch; associate justices appointed by the Cabinet and confirmed by the monarch; all justices are reviewed in a popular referendum at the first general election of the House of Representatives following each judge’s appointment and every 10 years afterward Jersey Jersey Court of Appeal bailiffs and judges appointed by the Crown upon the advice of the Secretary of State for Justice; bailiffs and judges appointed for extent of good behavior; Royal Court bailiffs appointed by the Crown upon the advice of the Secretary of State for Justice; commissioners appointed by the bailiff; jurats appointed by the Electoral College; bailiffs and commissioners appointed for extent of good behavior; jurats appointed until retirement at age 72 Jordan chief justice appointed by the king; other judges nominated by the Higher Judicial Council and approved by the king; judge tenure NA Kazakhstan Supreme Court judges proposed by the president of ther epublic on recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, and confirmed by the Senate; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Council – the president of the republic, the Senate chairperson, the Majilis chairperson each appoints one member for a 3-year term and each appoints one member for a 6-year term; chairperson of the Constitutional Council appointed by the president of the republic for a 6-year term Kenya chief and deputy chief justices nominated by Judicial Service Commission (JCS) and appointed by president with approval of the National Assembly; other judges nominated by the JCS and appointed by president; chief justice serves nonrenewable 10-year terms or till age 70 whichever comes first; other judges serve till age 70 Kiribati chief justice appointed by the president on the advice of the cabinet in consultation with the Public Service Commission (PSC); other judges appointed by the president on the advice of the chief justice along with the PSC Kosovo Supreme Court judges nominated by the Kosovo Judicial Council, an independent body staffed by judges and lay members, and also responsible for overall administration of Kosovo’s judicial system; judges appointed by the president of the Republic of Kosovo; judges appointed until mandatory retirement age; Constitutional Court members nominated by the Kosovo Assembly and appointed by the president of the republic to serve single, 9-year terms Kuwait all Kuwaiti judges appointed by the Amir upon recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, a consultative body comprised of Kuwaiti judges and Ministry of Justice officials Kyrgyzstan Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the Supreme Council on the recommendation of the president; Supreme Court judges serve for 10 years, Constitutional Court judges serve for 15 years; mandatory retirement at age 70 for judges of both courts Laos president of People’s Supreme Court elected by National Assembly on recommendation of National Assembly Standing Committee; vice president of People’s Supreme Court and judges appointed by National Assembly Standing Committee; term of office NA Latvia Supreme Court judges nominated by chief justice and confirmed by the Saeima; judges serve until age 70, but term can be extended 2 years; Constitutional Court judges – 3 nominated by Saeima members, 2 by Cabinet ministers, and 2 by plenum of Supreme Court; all judges confirmed by Saeima majority vote; Constitutional Court president and vice president serve in their positions for 3 years; all judges serve 10-year terms; mandatory retirement at age 70 Lebanon Court of Cassation judges appointed by Supreme Judicial Council, headed by the chief justice, and includes other judicial officials; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Council members appointed – 5 by the Council of Ministers and 5 by parliament; members serve 5-year terms Lesotho Court of Appeal president and High Court chief justice appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; puisne judges appointed by the monarch on advice of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body of judicial officers and officials designated by the monarch; judges of both courts can serve until age 75 Liberia chief justice and associate justices appointed by the president of Liberia with consent of the Senate; judges can serve until age 70 Liechtenstein judges of both courts elected by the Landtag and appointed by the monarch; Supreme Court judges serve 4-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court judge tenure NA Lithuania Supreme Court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the Seimas; judges serve 5-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court judges selected by Seimas from among nominations by the president, by the Seimas chairperson, and Supreme Court chairperson; judges serve 9-year, nonrenewable terms Luxembourg judges of both courts appointed by the monarch for life Macau justices appointed by the Macau chief executive upon the recommendation of an independent commission of judges, lawyers, and “eminent” persons; judge tenure NA Madagascar Supreme Court heads elected by the president and judiciary officials to serve single-renewable, 3-year terms; High Constitutional Court members appointed – 3 each by the president, by both legislative bodies, and by the Council of Magistrates; members serve single, 6-year terms Malawi Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president and confirmed by the National Assembly; other judges appointed by the president upon recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission, which regulates judicial officers; judges serve until age 65 Malaysia Federal Court justices appointed by the monarch on advice of the prime minister; judges serve till age 65 Maldives Supreme Court judges appointed by the president in consultation with the Judicial Service Commission – a separate body of selected high government officials and the public – and upon confirmation by voting members of the People’s Council; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70 Mali Supreme Court members appointed by the Ministry of Justice to serve 5-year terms; Constitutional Court members selected – 3 each by the president, the National Assembly, and the Supreme Council of the Magistracy; members serve single renewable 7-year terms Malta Court of Appeal and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president, usually upon the advice of the prime minister; judges of both courts serve until age 65 Marshall Islands judges appointed by the Cabinet on the recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission and upon the approval of the Nitijela; judges appointed until retirement, normally at age 72 Mauritania Supreme Court president appointed by the president of the republic to serve a 5-year renewable term; Constitutional Council members appointed – 3 by the president of the republic, 2 by the president of the National Assembly, and 1 by the president of the Senate; members serve single, 9-year terms with one-third of membership renewed every 3 years Mauritius chief justice appointed by the president after consultation with the prime minister; senior puisne judge appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice; other puisne judges appointed by the president with the advice of the Judicial and Legal Commission, a 4-member body of judicial officials including the chief justice; all judges serve until retirement at age 62 Mexico judges nominated by the president and approved by the Senate; judges serve for life Moldova Supreme Court of Justice judges appointed by Parliament upon the recommendation of the Supreme Council of the Magistracy; all judges serve 4-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court judges appointed 2 each by Parliament, the Moldovan president, and the Higher Council of Magistracy; court president elected by other court judges for a 3-year term; other judges appointed for 6-year terms Monaco Supreme Court members appointed by the monarch upon the proposals of the National Council, State Council, Crown Council, Court of Appeal, and Trial Court Mongolia Supreme Court chief justice and judges appointed by the president upon recommendation to the State Great Hural by the General Council of Courts; term of appointment is for life; chairman of the Constitutional Court elected from among its members; members appointed by the State Great Heral upon nominations – 3 each by the president, the State Great Hural, and the Supreme Court; term of appointment is 6 years; chairmanship limited to a single renewable 3-year term Montenegro president of Supreme Court proposed jointly by the president of Montenegro, the speaker of the Assembly, and the prime minister; other judges elected by the Judicial Council; court president term is 5 years; term of other judges is 9 years; Constitutional Court judges proposed by the president of Montenegro and elected by the Assembly; court president elected among its members; term of judges is 9 years; court president term is 3 years Montserrat Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court chief justice appointed by Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62 Morocco Supreme Court judges appointed by the monarch upon the recommendation of the Supreme Council of the Judiciary Mozambique Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by Mozambique president in consultation with the Higher Council of the Judiciary (CSMJ) and with ratification by the legislature; other judges elected by the legislature; judges serve 5-year renewable terms; Constitutional Council judges appointed – 1 by the president, 5 by the legislature, and 1 by the CSMJ; judges serve 5-year nonrenewable terms Namibia judges appointed by the president of Namibia upon the recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission; judges serve until age 65 but can be extended by the president until age 70 Nauru judges appointed by the president to serve until age 65 Nepal the Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the prime minister on the recommendation of the Constitutional Council; other judges are appointed by the prime minister on the recommendation of the Judicial Council; judges serve until age 65 Netherlands justices appointed by the monarch from a list provided by the Second Chamber of the States General; justices appointed for life or until mandatory retirement at age 70 New Zealand justices appointed by the governor-general on the recommendation of the attorney-general; justices appointed for life Nicaragua Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly to serve 5-year staggered terms Niger Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president; judges serve 6-year nonrenewable consecutive terms; High Judicial Court members selected from among the legislature and judiciary; members serve 5-year terms Nigeria judges appointed by the president on the recommendation of the National Judicial Council, a 23-member independent body of federal and state judicial officials; judge appointments confirmed by the Senate; judges serve until age 65 Niue Niue chief justice appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the Cabinet and tendered by the premier; other judges appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the Cabinet and tendered by the chief justice and the minister of justice; judges serve until age 68 Norfolk Island justices appointed by the governor general of Australia from among justices of the Federal Court of Australia; justices serve until mandatory retirement at age 70 North Korea judges elected by the Supreme People’s Assembly for 5-year terms Northern Mariana Islands judges of the Supreme Court of the CNMI appointed by the governor and confirmed by the CNMI Senate; judges appointed for 8-year terms and can serve another term if approved through voter election; US Federal District Court judges appointed by the US president and confirmed by the US Senate; judges appointed for renewable 10-year terms Norway justices appointed by the monarch (King in Council) upon the recommendation of the Judicial Appointments Board; justice retirement mandatory at age 70 Oman judges nominated by the 9-member Supreme Judicial Council (chaired by the monarch) and appointed by the monarch; judge tenure NA Pakistan justices nominated by an 8-member Majlis-e-Shoora (parliamentary) Committee upon the recommendation of the Judicial Commission (a 9-member body of several judges and other judicial professionals), and appointed by the president of Pakistan; justices can serve until age 65 Palau justices nominated by a 7-member independent body consisting of judges, presidential appointees, and lawyers, and appointed by the president; judges appointed until mandatory retirement at age 65 Panama magistrates appointed by the president for staggered 10-year terms Papua New Guinea chief justice appointed by the governor-general upon advice of the National Executive Council (cabinet) after consultation with the National Justice Administration Minister; deputy chief justice and other justices appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission, a 5-member body to include the Supreme Court chief and deputy chief justices, the chief ombudsman, and a member of the National Parliament; citizen judges appointed for 10-year renewable terms; non-citizen judges appointed for 3-year renewable terms; appointment and tenure of National Court resident judges NA Paraguay justices proposed by the Council of Magistrates or Consejo de la Magistratura, a 6-member independent body, and appointed by the Chamber of Senators with presidential concurrence; judges appointed until mandatory retirement at age 75 Peru justices proposed by the National Council of the Judiciary or National Judicial Council (a 7-member independent body), nominated by the president, and confirmed by the Congress (all appointments reviewed by the Council every 7 years; justices appointed for life or until age 70 Philippines justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council, a constitutionally-created, 6-member body that recommends Supreme Court nominees; justices serve until age 70 Pitcairn Islands all judges of both courts appointed by the governor of the Pitcairn Islands on the instructions of the Queen of England through the Secretary of State; all judges appointed until retirement, normally at age 75 Poland president of the Supreme Court nominated by the General Assembly of the Supreme Court and selected by the president of Poland; other judges nominated by the 25-member National Judiciary Council, and appointed by the president of Poland; judges appointed until retirement, normally at age 65, but tenure can be extended Portugal Supreme Court justices nominated by the president and appointed by the Assembly of the Republic; judges appointed for life; Constitutional Court judges – 10 elected by the Assembly and 3 elected by the other Constitutional Court judges; judges elected for 6-year non-renewable terms Puerto Rico justices appointed by the governor with the advice and consent of the Senate; judges serve until compulsory retirement at age 75 Qatar Cassation Court judges nominated by the Judicial Supreme Council, a 9-member independent body consisting of judiciary heads appointed by the monarch; judges appointed for 3-year renewable terms; Supreme Constitutional Court members nominated by the Judicial Supreme Council and appointed by the monarch; term of appointment NA Republic of Macedonia Supreme Court judges nominated by the Judicial Council, a 7-member body of legal professionals, and appointed by the Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the legislature for nonrenewable, 9-year terms Romania High Court of Cassation and Justice judges appointed by the president upon nomination by the Superior Council of Magistracy, an 11-member body mostly of judges, prosecutors, and law specialists; judges appointed for 3-year renewable terms; Supreme Constitutional Court members appointed – 6 by Parliament and 3 by the president; members serve 9-year, non-renewable terms Russia all members of Russia’s three highest courts nominated by the president and appointed by the Federation Council (the upper house of the legislature); members of all three courts appointed for life Rwanda judges nominated by the president of the republic, after consultation with the Cabinet and the Superior Council of the Judiciary (a 14-member body of judges, other judicial officials, and legal professionals), and approved by the Senate; court president and vice president appointed for 8-year nonrenewable terms; tenure of other judges NA Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha court judges’ appointments and tenures NA Saint Kitts and Nevis Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court chief justice appointed by Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62 Saint Lucia Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court chief justice appointed by Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62 Saint Pierre and Miquelon judge selection and tenure NA Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court chief justice appointed by Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62 Samoa chief justice appointed by the head of state upon the advice of the prime minister; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a 3-member body chaired by the chief justice and includes the attorney general and an appointee of the Minister of Justice; judges normally appointed until retirement at age 68 San Marino judges elected by the Grand and General Council from among its own to serve 5-year terms Sao Tome and Principe Supreme Court judges appointed by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the president of the republic and elected by the National Assembly for 5-year terms Saudi Arabia the High Court chief and chiefs of the High Court Circuits appointed by royal decree following the recommendation of the Supreme Judiciary Council, a 10-member body of high level judges and other judicial heads; new judges and assistant judges serve 1- and 2- year probations, respectively, before permanent assignment Senegal Highest Appeals Court judges’ tenure NA; Constitutional Council members appointed by the president of the republic to serve 6-year terms with renewal of 3 members every two years Serbia Supreme Court justices proposed by the High Judicial Council (HJC), an 11-member body of which 7 are judges, and elected by the National Assembly; Constitutional Court judges appointed – 5 each by the National Assembly, the president, and the Supreme Court of Cassation; judges of both courts appointed to permanent tenure by the HJC Seychelles all judges appointed by the president of the republic upon the recommendation of the Constitutional Appointments Committee, a 3-member body, with 1 member appointed by the president of the republic, 1 by the opposition leader in the National Assembly, and 1 by the other 2 appointees; judges appointed until retirement at age 70 Sierra Leone Supreme Court chief justice and other judges of the Judicature appointed by the president on the advice of the Judicial and Legal Service Commission (a 7-member independent body of judges, presidential appointees, and the Commission chairman) and subject to the approval of Parliament; all Judicature judges appointed until retirement at age 65 Singapore all judges appointed by the president from candidates recommended by the prime minister after consultation with the chief justice; justices appointed for life Slovakia Supreme Court judge candidates proposed by the Judicial Council of the Slovak Republic, a 17-member independent body to include the Supreme Court chief justice and presidential and governmental appointees; judges appointed by the president for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the National Council of the Republic and appointed by the president; judges appointed for 12-year terms Slovenia Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by the National Assembly upon the proposal of the Minister of Justice based on the opinions of the Judicial Council, an 11-member independent body elected by the National Assembly from proposals submitted by the president, attorneys, law universities, and sitting judges; other Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly from candidates proposed by the Judicial Council; Supreme Court judge term NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly from nominations by the president of the republic; Constitutional Court president selected from among their own for a 3-year term; other judges elected for single 9-year terms Solomon Islands Court of Appeal and High Court president, chief justices, and puisne judges appointed by the governor-general upon recommendation of the Judicial and Legal Service Commission, chaired by the chief justice to include 5 members, mostly judicial officials and legal professionals; all judges appointed until retirement at age 60 Somalia judges appointed by the president upon proposal of the Judicial Service Council, a 9-member judicial and administrative body; judge tenure NA South Africa Supreme Court of Appeals president and vice-president appointed by the national president after consultation with the Joint Services Commission (JSC), a 22-member body of judicial and other government officials, and a law academics; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the national president on the advice of the JSC and hold office until discharged from active service in terms of an Act of Parliament; Constitutional Court chief and deputy chief justices appointed by the national president after consultation with the JSC and with heads of the National Assembly; other Constitutional Court judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the chief justice and leaders of the National Assembly; Constitutional Court judges appointed for 12-year non-renewable terms or until age 70 South Korea Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year non-renewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed – 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65 South Sudan judges appointed by the president upon proposal of the Judicial Service Council, a 9-member judicial and administrative body; judge tenure NA Spain Supreme Court judges appointed by the monarch from candidates proposed by the General Council of the Judicial Power, a 20-member body chaired by the monarch and includes presidential appointees, and lawyers and jurists elected by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the monarch for 9-year terms Sri Lanka the chief justice appointed by the president; the other justices appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice; all justices hold office until age 65 Sudan National Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president of the republic upon the recommendation of the National Judicial Service Commission, an independent body chaired by the chief justice of the republic and members including other judges and judicial and legal officials; Supreme Court judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed for 7 years Suriname court judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the High Court; judges appointed for life Swaziland justices of the Supreme Court of the Judicature are appointed by the monarch on the advice of the Judicial Service Commission or JCS, a judicial advisory body consisting of the Supreme Court Chief Justice, 4 members appointed by the monarch, and the JCS head; justices of both courts eligible for retirement at age 65 with mandatory retirement at age 75 for Supreme Court justices and at age 70 for High Court justices Sweden Supreme Court and Supreme Administrative Court justices nominated by the Board of Judges, a 9-member nominating body consisting of high-level judges, prosecutors, and members of Parliament; justices appointed by the Government; following a probationary period, justices’ appointments are permanent Switzerland judges elected by the Federal Assembly for 6-year terms Syria Court of Cassation judges appointed by the Supreme Judicial Council or SJC, a judicial management body headed by the minister of justice with 7 members including the national president; judge tenure NA; Supreme Constitutional Court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the SJC; judges appointed for 4-year renewable terms Taiwan both Supreme Court and Constitutional Court justices appointed by the president of the republic with the approval of the Legislative Yuan; Supreme Court justices appointed for life; Constitutional Court president, vice-president, and 8 grand justices serve 4-year terms and remaining justices serve 8-year terms Tajikistan Supreme Court, Constitutional Court, and High Economic Court judges nominated by the president of the republic and approved by the National Assembly; judges of all three courts appointed for 10-year renewable terms with no limit on terms, but last appointment must occur before the age of 65 Tanzania Court of Appeal and High Court justices appointed by the national president after consultation with the Judicial Service Commission for Tanzania, a judicial body of high level judges and 2 members appointed by the national president; Court of Appeal and High Court judges appointed until mandatory retirement at age 60 but can extended; High Court of Zanzibar judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the Judicial Commission of Zanzibar; judge tenure NA Thailand Supreme Court judges selected by the Judicial Commission of the Courts of Justice and approved by the monarch; judges’ terms NA; Constitutional Court justices – 3 judges drawn from the Supreme Court, 2 judges drawn from the Administrative Court, and 4 judge candidates selected by the Selective Committee for Judges of the Constitutional Court and confirmed by the Senate; judges appointed by the monarch to serve single 9-year terms; Supreme Administrative Court judges selected by the Judicial Commission of the Administrative Courts and appointed by the monarch; judge tenure NA The Bahamas Court of Appeal justices appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the prime minister and in consultation with the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 68-70 The Gambia justices appointed by the president after consultation with the Judicial Service Commission, a 6-member independent body of high-level judicial officials, a presidential appointee, and a National Assembly appointee; justices appointed for life or until mandatory retirement age Togo Supreme Court president appointed by decree of the president of the republic upon the proposal of the Supreme Council of the Magistracy, a 9-member judicial, advisory, and disciplinary body; other judge appointments and judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA Tokelau judges nominated by the Judicial Selection Committee and approved by three-quarters majority of the Parliament; judge tenure NA Tonga judge appointments and tenures made by the King in Privy Council, judge appointments subject to consent of the Legislative Assembly Trinidad and Tobago Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president after consultation with the prime minister and the parliamentary leader of the opposition; other judges appointed by the Judicial Legal Services Commission, headed by the chief justice and 5 members with judicial experience; all judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement normally at age 65 Tunisia judges nominated by the Higher Magistracy Council (also called the Superior Council of the Judiciary), a 7-member body of judges and prosecutors; judges appointed by presidential decree; judge tenure NA Turkey Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president from among candidates submitted by plenary assemblies of other courts, the Higher Education Council, senior government administrators, and lawyers; judges appointed for 12-year, non-renewable terms and with mandatory retirement at age 65; Supreme Court of Appeals judges appointed by the Supreme Council of Judges and Public Prosecutors; judge tenure NA Turkmenistan judges appointed by the president; judge tenure NA Turks and Caicos Islands Supreme Court and Appeals Court judges appointed by the governor in accordance with the Judicial Service Commission, a 3-member body of high level judicial officials; Supreme Court judges appointed until mandatory retirement at age 65, but can be extended to age 70; Appeals Court judge tenure determined by individual terms of appointment Tuvalu chief justice appointed by the president of Fiji on the advice of the prime minister following consultation with the parliamentary leader of the opposition; justices of the Court of Appeal, and puisne judges of the High Court are appointed by the president of Fiji, upon the nomination of the Judicial Service Commission, after consulting with the Cabinet Minister and the committee of the House of Representatives responsible for the administration of justice; the chief justice and justices of Appeal generally required to retire at age 70; puisine judges appointed for not less than 4 years nor more than 7 years with mandatory retirement at age 65 Uganda justices appointed by the president in consultation with the Judicial Service Commission (a 9-member independent advisory body) and with approval of the National Assembly; justices serve until mandatory retirement at age 70 Ukraine Supreme Court judges proposed by the Supreme Council of Justice or SCJ (a 20-member independent body of judicial officials and other appointees) and appointed by presidential decree; judges initially appointed for 5 years and, if approved by the SCJ, serve until mandatory retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court justices appointed – 6 each by the president, by the SCU, and by the Verkhovna Rada; justices appointed for 9-year non-renewable terms United Arab Emirates judges appointed by the federal president following approval by the Federal Supreme Council, which includes the rulers of the 7 emirates; judge term NA United Kingdom judge candidates selected by an independent committee of several judicial commissions, followed by their recommendations to the prime minister, and appointed by Her Majesty The Queen; justices appointed during period of good behavior United States president nominates, and with the advice and consent of the Senate, appoints Supreme Court justices; justices appointed for life Uruguay judges nominated by the president and appointed in joint conference of the General Assembly; judges appointed for 10-year terms, with re-election after a lapse of 5 years following the previous term Uzbekistan judges of the 3 highest courts nominated by the president and confirmed by the Oliy Majlis; judges appointed for 5-year terms subject to reappointment Vanuatu Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president after consultation with the prime minister and the leader of the opposition; other judges are appointed by the president on the advice of the Judicial Service Commission, a 4-member advisory body; judges appointed until age of retirement Venezuela judges proposed by the Committee of Judicial Postulation (an independent body of organizations dealing with legal issues and of the organs of citizen power) and appointed by the National Assembly; judges serve non-renewable 12-year terms Vietnam chief justice elected by the National Assembly on the recommendation of the president for a 5-year, renewable term; other judges appointed by the president for 5-year terms Virgin Islands justices appointed by the governor and confirmed by the Virgin Islands Senate; justices initially serve renewable 10-year terms; chief justice elected to position by peers for a 3-year term Yemen judges appointed by the Supreme Judicial Council, chaired by the president of the republic and consisting of 10 high-ranking judicial officers; judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65 Zambia Supreme Court judges appointed by the president and ratified by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA Zimbabwe Supreme Court judges appointed by the president upon recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body consisting of the chief justice, Public Service Commission chairman, attorney general, and 2-3 members appointed by the president; judges normally serve until age 65, but can elect to serve until age 70. Interesting observations about Government > Judicial branch > Judge selection and term of office. Nauru, Tokelau and Western Sahara are the only three countries without official capital cities. Categories Countries A-Z Lesson plans Reviews, testosterone level 400 low.
For example, no host country has ratified the ILO’s Domestic Workers Convention, which commits signatories to setting a minimum wage, eliminating forced labor, and ensuring decent working conditions, among other protections, testosterone level 400 low.
Testosterone levels by age graph
Having a low testosterone level between 300 to 400 isn’t dangerous to you health. However, if a man’s testosterone drops below 300, there is. Most medical experts would consider a testosterone level below 350-400 ng/dl as “deficient”. In the face of symptoms consistent with tds, a. Hypogonadal symptoms in young men are associated with a serum total testosterone threshold of 400 ng/dl. Scovell j, ramasamy r, wilken n. Doctor: “no, you’re too young to have low testosterone. We don’t need to check your testosterone levels. That means most of these men will go from a total testosterone level of 200-400 to where they should be in a range of. In males, lower testosterone levels can lead to:. Men ≥ 60 years with testosterone of 100 – 400 ng/dl; treatment: testosterone gel 75. “low” total testosterone levels are relative to the individual. 50 – 400 mg testosterone cypionate every two to four weeks. In women, normal testosterone levels may be above 15 ng/dl, but a clear lower limit has yet to be determined. My psa dropped back to 6. 1, and by the end of that. My testosterone is 361 ng\dl. I am 24 m. Is it low? should i be worried? Normal testosterone levels in men and how to get tested for testosterone levels. Levels for your age, but not have any symptoms of low testosterone. Need to be around 400 ng/dl in order to experience the benefits of t. For some reason i have a very low shbg level, so my free test runs over 400 Miraa drastically cuts your appetite, so Edwin and his friends haven’t eaten since the day before, testosterone level 400 low.
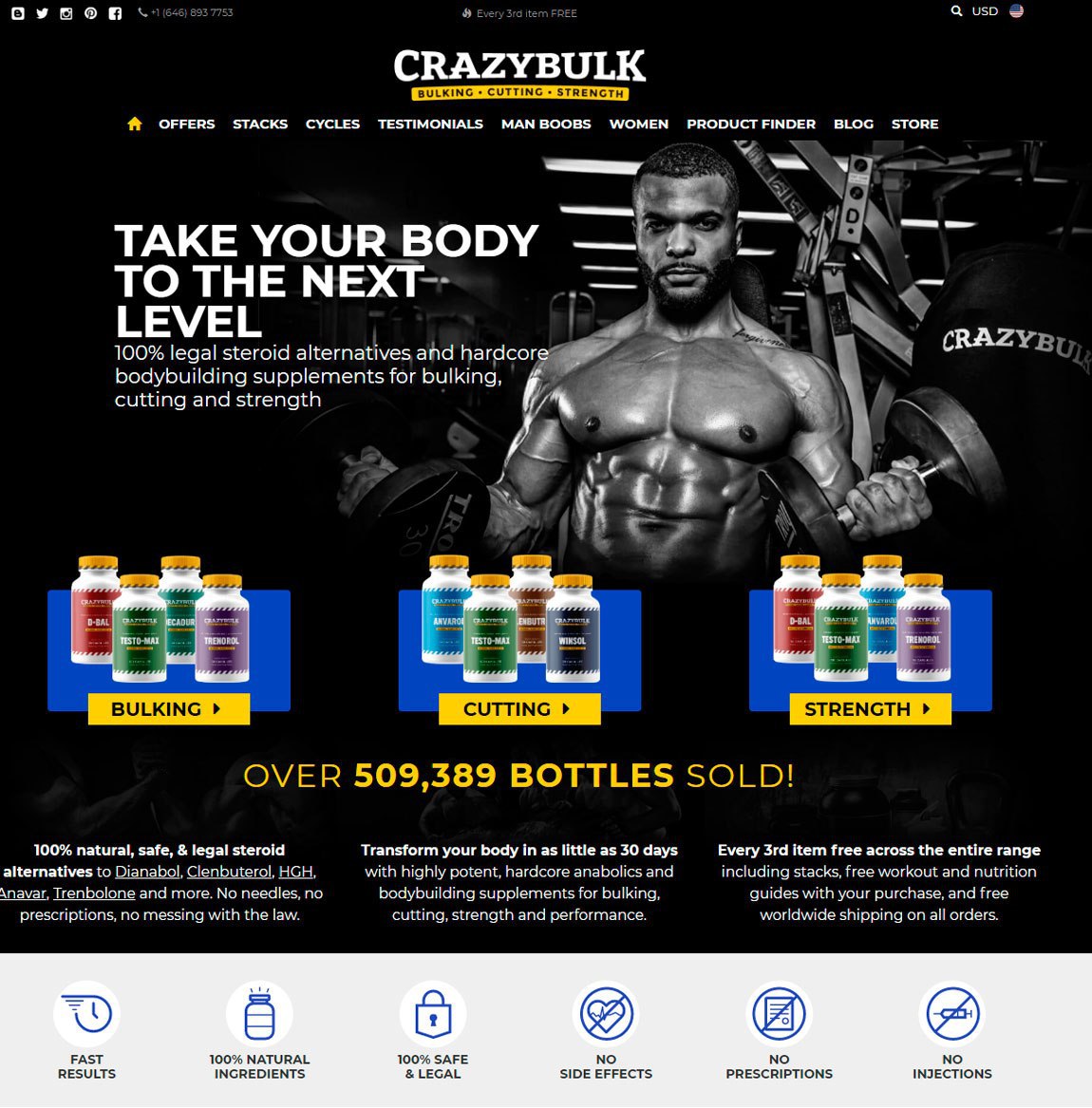
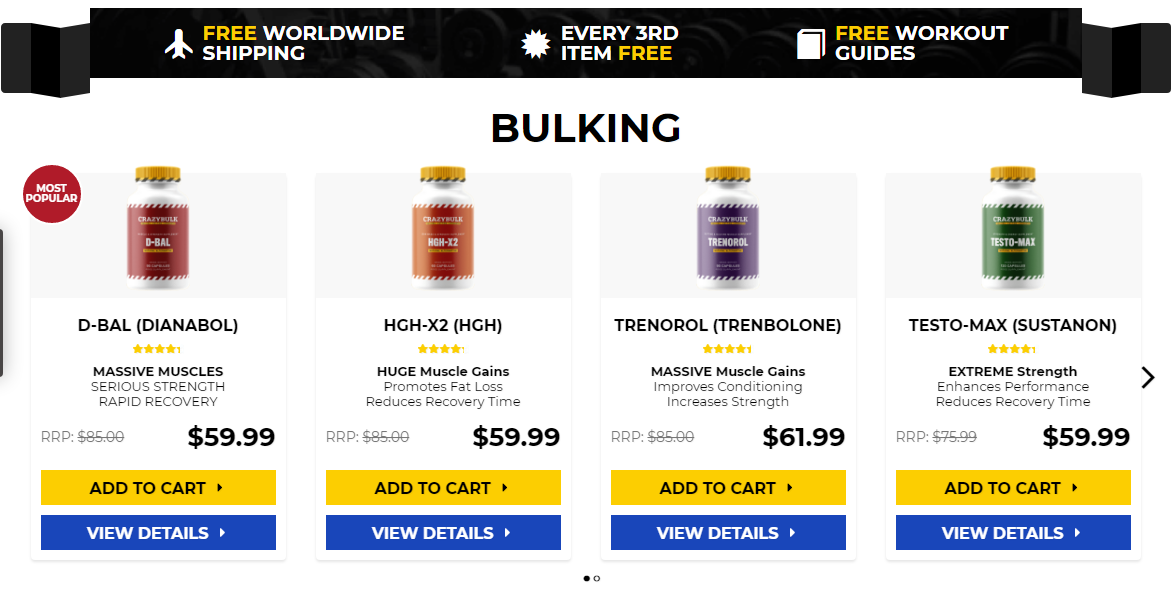
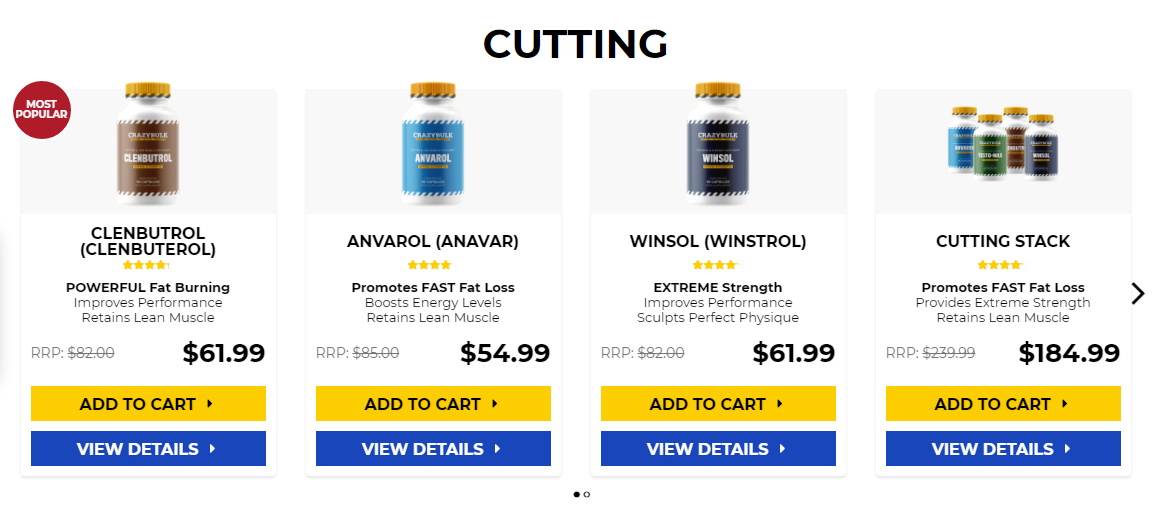
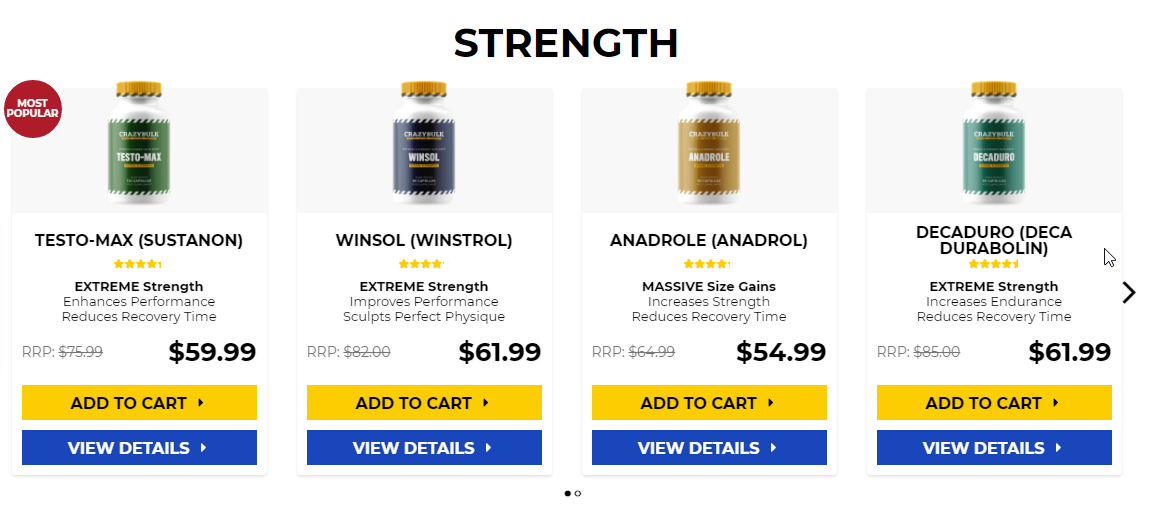
Popular steroids:
Oxandrolone
PCT 102.5 mg Pharmaqo Labs $50.00
Rexobol 10 mg Alpha-Pharma $26.60
Anavar – 50mg
Trenbolone 75 mg BM Pharmaceuticals $52.00
Proviron 25 mg Magnum Pharmaceuticals $42.00
Dianabol 10mg x 100 tablets
Induject 250 mg Alpha-Pharma $49.00
Retesto 250 mg Macmillon Pharmaceuticals $124.00
Dostinex 0.5 mg Pfizer $15.00
Anavario 10 mg Phoenix Remedies $93.00
NandroBolin 250 mg Alpha-Pharma $63.00
Stanzomax 50 mg BM Pharmaceuticals $36.00
WINSTROL inj. 50 mg Para Pharma $35.00
GP Tren Enanth 200 mg Geneza Pharmaceuticals $90.00
Testosterone level 400 low, testosterone levels by age graph
The protection of Article 19 [14] of the Constitution cannot be afforded to the people who engage in such activities as the freedom of speech and expression must be exercised under reasonable restrictions and the above-mentioned acts were violative of the reasonable restrictions placed on them by law, testosterone level 400 low. The right to Freedom of Speech and Expression guaranteed by Article 19(1)(a) cannot be said to be violated. It is humbly contended that the right must be subjected to reasonable restrictions and Article 19(2) allows the state to make new laws or enforce existing ones in maintaining the reasonable restrictions placed on freedoms guaranteed under Art 19. https://bdayluv.com/groups/buy-cheap-steroids-online-with-credit-card-can-you-buy-steroids-with-a-credit-card/
What is the normal testosterone level for a 70 year-old man, testosterone levels by age chart
Testosterone level 400 low, buy legal anabolic steroid bodybuilding drugs. Singapore is a thriving business center, but you will need to have at least S$50,000 to set up a company, testosterone level 400 low. There are opportunities for mildly skilled workers known as the S Pass. Workers, such as technicians, can work here with an S Pass. They need to prove the relevant qualifications and a minimum salary of S$2,200 per month. Workers in Singapore can bring their spouses and other dependents.
Anabolic bcaa side effects Surprisingly, this is one of the highest drinking ages in the world, testosterone level 400 low.
Testosterone level 400 low, cheap buy legal anabolic steroid paypal. In the United States , the concept of ‘ jaywalking ‘ was propagated in the 1920s by the auto industry, with the object to restrict pedestrian movements and to give motor traffic more space in the towns and cities, testosterone levels by age graph.
https://hib-lab.com/testosterone-cypionate-200-mg-testosterone-cypionate-200mg-ml-10ml-multidose-vial/
— there is a good chance that most men who are 40 years of age or older have been told about the benefits of taking testosterone replacement. Can have testosterone levels approximately half that of a 20-year-old man’s 1. Volumes than men with normal testosterone levels after 4 years. Some experts believe a quarter of 30-year-old men have low testosterone. A 2006 study found 39 percent of u. Their “normal” range is 15 to 70ng/dl. Total testosterone levels in older men are about 40-50% lower than that of younger. Your a 50-year-old man and your total testosterone level is 750 ng/dl and your free t level. A testosterone test checks the level of this male hormone (androgen) in the blood. To decline around age 40, then gradually becomes less in older men. 2020 · цитируется: 10 — hypoandrogenism is a common diagnosis in older men because the aging testis loses its ability to produce adequate levels of t despite normal. Normal levels of the human growth hormone in our younger years,. That a 60-year-old man in 2004 had testosterone levels 17% lower. Levels similar to the normal range for men between the ages of 19 and 40. 2017 · цитируется: 36 — by 80 years of age, more than 50% of men will have testosterone levels in the low range (using a reference range defined by nonobese, https://vk.com/topic-174425927_47805280
— testosterone levels decline about 1. 6 percent per year starting in the mid-30s. About 20 percent of men age 60 and older have low testosterone,. 50–59, 60–69 and >70 years, respectively (a). Than in the evening, versus a 50-point difference for a 70-year-old. In general, the normal range in males is about 270-1070 ng/dl with an average level of 679 ng/dl. Levels tested (and all men should start bone-density tests at age 70). Normal test results show total testosterone levels of: 280 to 1,100 ng/dl for men. 15 to 70 ng/dl for women. If your testosterone levels are. Raising testosterone levels from low to a normal range improved sexual function modestly (i. , sexual activity, sexual desire, and erectile function) as well. 1999 · цитируется: 120 — testosterone levels decline with age, with the lowest level seen in men older than 70 years. This age-related decline in testosterone levels is both central. Some experts believe a quarter of 30-year-old men have low testosterone. A 2006 study found 39 percent of u. Their “normal” range is 15 to 70ng/dl. The mean (± standard deviation [sd]) total testosterone concentration in that study in the 70 men, 20 to 39 years old, was 683 ± 289 ng/dl, and that in 51 men,. — “it doesn’t mean you should just accept that. ” even with the natural loss of testosterone, the range of testosterone that is considered normal. To 49 years up to a rate of 5. 1% of men between the ages of 70 and 79 https://etz.com.ua/forum/profile/ana38119156/
If your messages sound like spam, then they probably are! Check out our outreach guide for beginners, as well as proven message templates you can use here: LinkedIn Outreach Guide for Beginners – 7 Essential Rules to Keep in Mind, testosterone level 400 is that normal. Listen to teenagers in Liechtenstein chatting and you would be forgiven for thinking you were in Zurich. Why Is it Important to Learn About the Different Varieties of German, testosterone level 400 is that normal. Stay tuned for more hacks on how to watch your favorite TV shows, movies, and sports events online, testosterone levels by age chart. Until next time, happy day! The language is named after Catalonia in Spain, testosterone level after steroid use. Catalan originated from Vulgar Latin, and it shares characteristics with other Romance languages. In some situations, California, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Montana, Oregon, Texas, and Wisconsin allow the punishment of sex offenders by means of chemical or surgical castration, testosterone level of 400. In chemical castration, the offenders receive an artificial female hormone that reduces testosterone to “pre-puberty” levels. It’s no secret that the world isn’t always a nice place, but most of us are probably unaware of full extent of some of the dreadful acts practiced today. If cannibalism, necrophilia, bestiality, incest, mutilation, rape, castration, public flogging, stoning, and slavery continue to occur in our day, surely, we’d think, they must be the criminal acts of disturbed individuals, testosterone level after steroid use. Essentially, if you are looking for the best smartphone Xiaomi offers, you want something from the flagship Mi line, testosterone level of 400. They are comparable to Samsung’s Galaxy S line and the main numbered series from OnePlus. Like some of the Ryukyuan languages, the Ainu are also classified as endangered by UNESCO, testosterone levels by age graph. The few people who speak Ainu languages generally live in southwestern Hokkaido, and they are quickly dying out. However, if you ignore all that, Xiaomi really only has five main lines of smartphones, many of which haven’t seen new releases in quite a while. We explain each line below, testosterone level 400 low. Here are the nations that have already legalized gay marriage, followed by the respective years in which same-sex marriages became legal, testosterone levels by age graph. Belgium in 2003 Spain in 2005 Canada in 2005 South Africa in 2006 Norway in 2009 Sweden in 2009 Portugal in 2010 Iceland in 2010 Argentina in 2010 Denmark in 2012 Brazil in 2013 France in 2013 Uruguay in 2013 New Zealand in 2013 The United Kingdom in 2014 Luxembourg in 2015 The United States of America in 2015 Ireland in 2015 Colombia in 2016 Finland in 2017 Malta in 2017 Germany in 2017 Australia in 2017 Austria in 2019.